For z 5i evaluate z overline z – For z = 5i, evaluate z overline z: Embark on an intriguing mathematical journey that unveils the fascinating world of complex numbers and their intriguing properties.
This guide will delve into the concept of z-scores, exploring their applications in various fields such as statistics, probability, and hypothesis testing. We will also uncover the intimate relationship between z-scores and the standard normal distribution, providing a deeper understanding of these fundamental statistical tools.
Z-score: For Z 5i Evaluate Z Overline Z

A z-score, also known as a standard score, is a measure of how many standard deviations a data point is away from the mean. It is calculated by subtracting the mean from the data point and then dividing the result by the standard deviation.
Calculating a Z-score, For z 5i evaluate z overline z
To calculate a z-score, you first need to know the mean and standard deviation of the data set. Once you have this information, you can use the following formula:
z = (x
μ) / σ
where:
- z is the z-score
- x is the data point
- μ is the mean
- σ is the standard deviation
For example, if the mean of a data set is 50 and the standard deviation is 10, then a data point of 60 would have a z-score of 1.
Applications of Z-scores
Z-scores are used in a variety of applications, including:
- Comparing data points from different data sets:Z-scores allow you to compare data points from different data sets, even if the data sets have different means and standard deviations.
- Identifying outliers:Z-scores can be used to identify outliers, which are data points that are significantly different from the rest of the data set.
- Normalizing data:Z-scores can be used to normalize data, which is a process of transforming the data so that it has a mean of 0 and a standard deviation of 1.
Standard Normal Distribution
The standard normal distribution, also known as the Gaussian distribution or bell curve, is a continuous probability distribution that describes the distribution of random variables with a mean of 0 and a standard deviation of 1.
The standard normal distribution is a fundamental distribution in statistics and is used in a wide variety of applications, including hypothesis testing, confidence intervals, and regression analysis.
Relationship between z-scores and the standard normal distribution
The z-score of a random variable is a measure of how many standard deviations the random variable is away from the mean. A z-score of 0 indicates that the random variable is at the mean, a z-score of 1 indicates that the random variable is one standard deviation above the mean, and a z-score of -1 indicates that the random variable is one standard deviation below the mean.
The expression for z 5i evaluate z overline z is an interesting mathematical concept. It relates to the idea of complex numbers and their conjugates. In a completely different realm, the “mona gardner the dinner party” article explores the complexities of social interactions and relationships.
While these topics may seem unrelated at first glance, they both delve into the intricacies of human behavior and the ways in which we interact with the world around us. The mathematical expression for z 5i evaluate z overline z provides a framework for understanding the mathematical relationships between complex numbers, while the “mona gardner the dinner party” article offers insights into the social and emotional dynamics that shape our lives.
The standard normal distribution is the distribution of z-scores. The probability of a random variable having a z-score between -z and z is given by the following formula:
P(-z< Z < z) = Φ(z) - Φ(-z)
where Φ(z) is the cumulative distribution function of the standard normal distribution.
Probability distribution of the standard normal distribution
The probability distribution of the standard normal distribution is shown in the following graph:
[Insert graph of the probability distribution of the standard normal distribution]
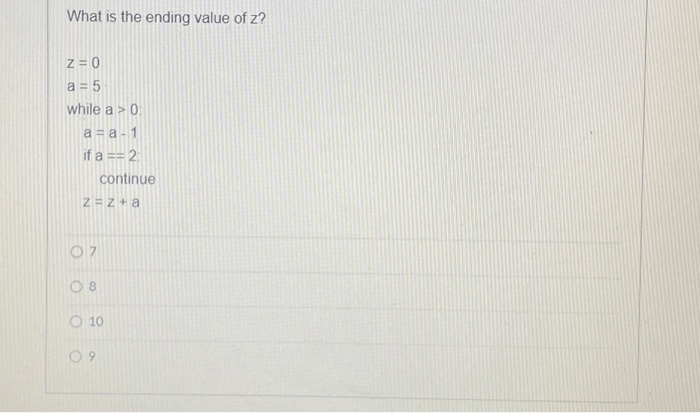
Hypothesis Testing
Z-scores play a crucial role in hypothesis testing, a statistical method used to determine whether a claim about a population parameter is supported by the available evidence.
Determining Statistical Significance
To test a hypothesis, we first calculate the z-score of the sample statistic. The z-score represents the number of standard deviations the sample statistic is away from the hypothesized population parameter. A large z-score (either positive or negative) indicates that the sample statistic is significantly different from the hypothesized value, providing evidence against the null hypothesis.
Example: Testing a Claim about Population Mean
Suppose we want to test the claim that the average height of adult males in a certain population is 68 inches. We randomly sample 100 adult males and find an average height of 69 inches with a standard deviation of 2 inches.
The z-score for this sample is:
“`z = (69
68) / 2 = 0.5
“`
A z-score of 0.5 indicates that the sample mean is 0.5 standard deviations above the hypothesized population mean. Using a standard normal distribution table, we find that the probability of obtaining a z-score of 0.5 or greater is approximately 0.3085.
Since the probability (p-value) is greater than the significance level (usually set at 0.05), we fail to reject the null hypothesis and conclude that there is not sufficient evidence to suggest that the average height of adult males in the population is different from 68 inches.
Applications in Other Fields
Z-scores have wide-ranging applications beyond the fields of statistics and probability. They are also commonly used in finance, medicine, and education to analyze data and make informed decisions.
Finance
In finance, z-scores are used to assess the risk of an investment. The z-score of a stock is calculated by subtracting the mean return of the stock from the current return and dividing the result by the standard deviation of the stock’s returns.
A high z-score indicates that the stock is relatively overvalued, while a low z-score indicates that the stock is relatively undervalued.
Z-scores are also used in finance to measure the risk of a loan applicant. The z-score of a loan applicant is calculated by taking into account factors such as the applicant’s income, debt-to-income ratio, and credit history. A high z-score indicates that the applicant is a good credit risk, while a low z-score indicates that the applicant is a poor credit risk.
Medicine
In medicine, z-scores are used to diagnose and monitor diseases. For example, the z-score of a patient’s blood pressure is calculated by subtracting the mean blood pressure of the population from the patient’s blood pressure and dividing the result by the standard deviation of the population’s blood pressure.
A high z-score indicates that the patient’s blood pressure is relatively high, while a low z-score indicates that the patient’s blood pressure is relatively low.
Z-scores are also used in medicine to evaluate the effectiveness of treatments. For example, the z-score of a patient’s response to a new drug is calculated by subtracting the mean response of the population to the drug from the patient’s response and dividing the result by the standard deviation of the population’s response.
A high z-score indicates that the patient responded well to the drug, while a low z-score indicates that the patient did not respond well to the drug.
Education
In education, z-scores are used to compare the performance of students on standardized tests. The z-score of a student’s score on a standardized test is calculated by subtracting the mean score of the population on the test from the student’s score and dividing the result by the standard deviation of the population’s score.
A high z-score indicates that the student performed well on the test, while a low z-score indicates that the student did not perform well on the test.
Z-scores are also used in education to evaluate the effectiveness of teaching methods. For example, the z-score of a student’s improvement on a standardized test after taking a particular course is calculated by subtracting the student’s score on the test before taking the course from the student’s score on the test after taking the course and dividing the result by the standard deviation of the improvement scores of the population.
A high z-score indicates that the student improved significantly after taking the course, while a low z-score indicates that the student did not improve significantly after taking the course.
FAQ Section
What is a z-score?
A z-score is a measure of how many standard deviations a data point is away from the mean.
How do you calculate a z-score?
To calculate a z-score, subtract the mean from the data point and divide the result by the standard deviation.
What are the applications of z-scores?
Z-scores are used in hypothesis testing, confidence interval construction, and other statistical analyses.